Are you searching for a sustainable way to replace overfishing and fish farms? Aquaponics can be the solution to polluted supermarket fish! It's a sustainable, eco-friendly approach for producing healthy food at home without hurting the environment. In this article, you'll find out what aquaponics is and how it works.
What is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics Fundamentals
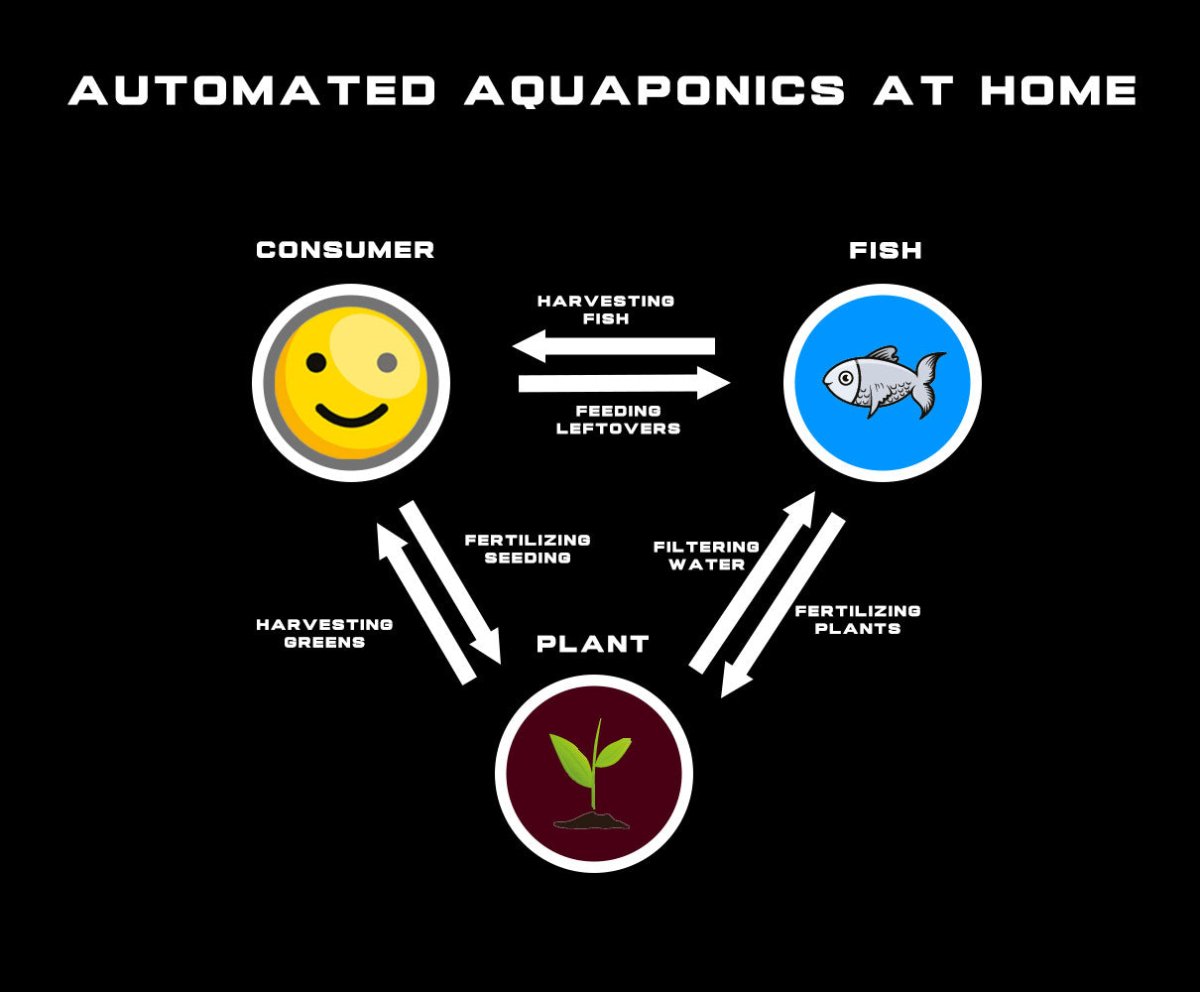
Aquaponics is a sustainable and innovative way to cultivate fish and plants together. Fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants filter the water for the fish. This means no more traditional soil-based farming!
Basic of Aquaponics
Aquaponics consists of a few key elements: Fish Tank, Grow Bed, and Bacteria. Here's a breakdown:
|
Component |
Description |
|
Fish Tank |
Houses aquatic species like fish and shrimp, which produce waste |
|
Grow Bed |
Contains the planting medium where plants get nutrients |
|
Bacteria |
Beneficial microbes that turn fish waste into plant available form |
Unique Aquaponics Details
Aquaponics is great for the environment. It requires minimal water and can be done indoors or outdoors. It also creates a highly effective and productive system due to the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
Call-to-action
Learn how aquaponics can revolutionize food production while saving natural resources. Get involved in this revolutionary technique today and help reduce our global reliance on overfishing and conventional fish farms. Don't miss out on this chance to make a positive impact on the planet's future.
Overfishing - Global Crisis caused by Trawlers?
Overfishing is a global crisis caused by trawlers and it's causing serious damage. As most fishing companies only care about how much fish they can pull out, the consequences of their actions are overlooked. These vessels are depleting marine resources, disrupting ecosystems, compromising biodiversity, destroying ocean ground and undermining food security for fishing communities. Plus, they're pushing commercially valuable species to the brink of extinction. Trawling techniques also create massive amounts of bycatch, including juvenile fish and species crucial to the balance of the environment. This unsustainable approach jeopardizes fishermen's livelihoods.
An estimated 1 trillion fish are caught from the wild yearly and about 100 billion gets dumped back.
Aquaponics offers a solution. It's a combination of aquaculture (cultivating fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil). This closed-loop system uses less water and increases food production efficiency.
In Singapore, the Sky Greens Farms has put this system into practice. By farming fish and growing plants in the same space, they are reducing reliance on conventional agriculture and minimizing pressure on marine resources. Aquaponics is a great way to find fish friends without threatening the ocean.
Aquaculture Alternative to Ocean Caught Fish?
Aquaculture - Is it a Viable Solution to Overfishing and Fish Farms?
Aquaculture provides an eco-friendly option for getting fish, by using controlled environments to cultivate species. It reduces the environmental damage caused by overfishing and lowers the reliance on fish farms.
Production of Aquaculture and Wildcaught Table:
|
Fish Species |
Aquaculture Production (metric tons) |
Wild Caught Production (metric tons) |
|
Pangasius |
3,100,000 |
2,000 |
|
Salmon |
2,800,000 |
705,000 |
The table shows that aquaculture production of pangasius and salmon is almost ten times higher than ocean caught production. This means we can meet the demand for fish without harming the environment.
Aquaculture also prevents some of the potential water pollution and run-offs if good waste handling systems are in place. It also helps in monitoring fish health and controlling diseases.
Pro Tip: Aquaponics is a combination of fish farming and hydroponics, where the waste from fish provides nutrients for plants, and plants filter the water for fishes. Try this innovative approach for effective results.
Harm of Farmed Salmon Compared to Home Made Fish
Fish farmed salmon versus home made fish - what's the difference? Fish farming is often seen as a more sustainable option than wild-caught fish. However, it has several harmful impacts. Let's explore them.
The fish feed for farmed salmon consists of processed pellets with antibiotics, preservatives, other chemicals and wild caught fish. While home made fish feed mostly on natural sources.
Farmed salmon cages can pollute the ocean floor, damaging the surrounding ecosystem. In contrast, home made fish have no impact on the ocean.
Farmed Norwegian Salmon World’s Most Toxic Food
Overcrowded fish farms create ideal conditions for disease. This leads to the use of more antibiotics. Homemade fish have a lower risk of disease spread due to their controlled environment and the sanitizing effect of the plants, worms and the grow bed.
Escaped farmed salmon can negatively affect native fish populations and become an invasive species. They also spread deadly diseases to wild populations. Home made fish pose no risk of disrupting natural ecosystems.
We must consider the harmful effects of fish farming on both the environment and our health. We can make informed choices about our seafood consumption by understanding these impacts.
Make a conscious decision when choosing farmed versus home made fish. Opt for sustainable alternatives that prioritize environmental conservation and personal well-being. Seafood choices you make can have a positive impact. Aquaponics proves that even fish prefer working from home!
Automated aquaponics system with multiple connected container
Automated aquaponics system with multiple connected container one month later
Hydroponics Completing the Cycle
Aquaponics revolutionizes agriculture by combining hydroponics and aquaculture - creating a self-sustaining ecosystem. This integration brings improved water efficiency, with studies showing up to 90% less water consumption. Plus, it eliminates synthetic fertilizers - reducing pollution and costs for farmers.
Pro Tip: Aquaponics not only mitigates overfishing, but also enables sustainable food production with fewer impacts on the environment. Common failure? If your fish start doing the backstroke, it's time to check your water quality!
Common Failures and How to Prevent Them
Aquaponics: Achieving Success and Avoiding Common Pitfalls
To guarantee success with an aquaponics setup, you must be aware of and beat common challenges. Six major points to consider are:
- Overfeeding: Always start off with feeding very little and adapt the amounts over time. Uneaten feed can rot very fast and pollute the water.
- Stopping Pests: Regularly checking the health of plants and keeping it clean will help ward off pests.
- Dealing with Diseases: Keeping good water quality, monitoring fish health, and being hygienic minimizes the risk of diseases.
- Prevent Overcrowding: Maintaining a balanced fish-to-plant ratio ensures optimal growth and prevents overcrowding, which affects water quality and stresses organisms.
- Establishing Stability: Slowly introducing fish and plants into the system enables them to settle in properly, grow steadily and give the bacteria enough time to adapt.
- Monitoring Water Parameters: Regularly testing and adjusting temperature, pH levels, dissolved oxygen, and nutrient levels is a great way to ensure a stable environment for both fish and plants but not necessary.
- Checking Nutrient Levels: Replenishing essential nutrients maintains the right balance and leads to healthy plant growth with micronutrient mix like rock dust.
Apart from these common pitfalls and their solutions, it's also important to remember that aquaponics systems require careful attention to detail. This means doing regular maintenance tasks like cleaning inlet filters, inspecting pumps, looking over plumbing connections, and maintaining system hygiene.
An example highlighting the significance of managing these aspects involves a small-scale aquaponics lover who initially failed to do regular water parameter testing. This led to uneven nutrient levels and stunted plant growth. By closely monitoring nutrient levels afterward, and tending to the system quickly, they were able to revive their plants and maintain a thriving aquaponics setup.
Plants Not Allowed
Plants you should exclude from aquaponics are either too large like many fruit trees and bushes, don't work with hydroponics like many root crops as they need deep grow beds, or disrupt the balance of the ecosystem. Such plants are called overdominant and unfit.
|
Too Big Plants |
Root Crops |
Overdominant Plants |
Prefer Dry Conditions |
Need Specific Conditions |
|
Sunflowers |
Potatoes |
Mint |
Lavender |
Chrysanthemums |
|
Corn |
Onions |
Watercress |
Rosemary |
Blueberries |
|
Pumpkins |
Ginger |
Bamboo |
Sage |
Grapes |
|
Blackberries |
Carrots |
Thyme |
Peppers |
Even though those plants usually don’t grow well in an aquaponics system, there are ways to make it work for almost any plants by playing with factors like grow medium, water timing, and nutrition composition for the plants.
Disadvantages of Aquaponics
Aquaponics may require a substantial upfront investment and limit the variety of fish that can be grown. Electricity is also needed for components such as heaters and lighting. Plus, certain crops are seasonal which reduces diversity and availability in certain regions.
In spite of its advantages, aquaponics can be difficult to set up and requires some basic knowledge to maintain. Prospective farmers must assess their resources, skills, and goals to see if it's suitable.
Don't miss out on this! Aquaponics can revolutionize farming while being eco-friendly and self-sustaining. Embrace the future of agriculture at your home now!
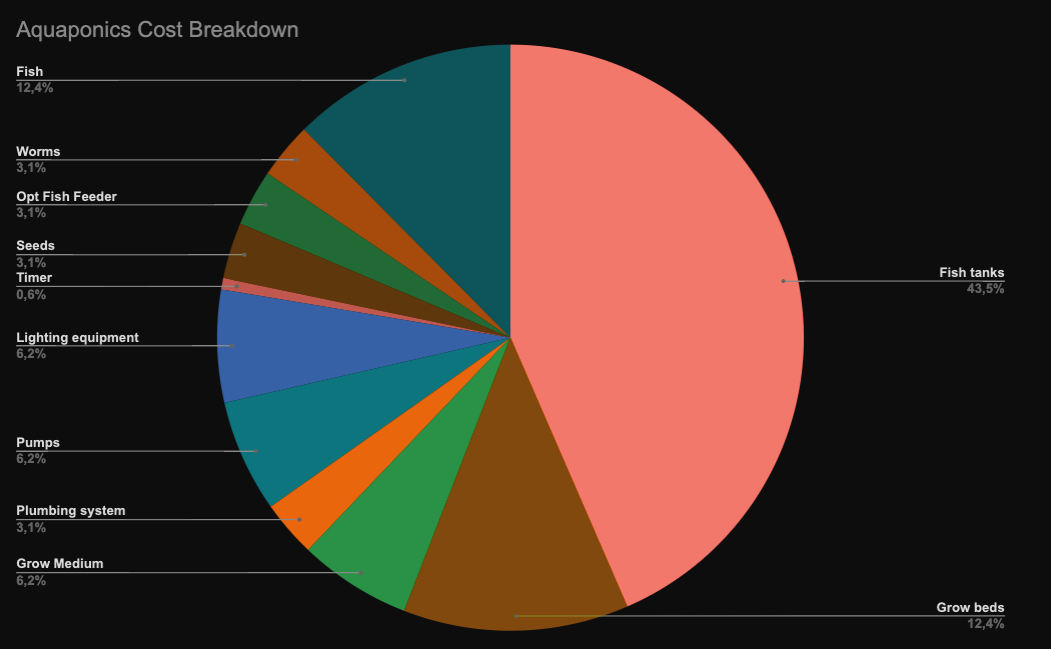
Ready to explore the cost of aquaponics? Get your calculator and fish jokes ready - make sustainability profitable!
Benefits of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is an innovative circular system that offers many advantages. It eliminates water waste by using the nutrient-rich water from fish tanks to fertilize plants. This makes it more efficient and sustainable. It can be adapted to individual needs, reducing the need for chemicals, single use plastic and transportation costs. Plus, it allows for local production and year-round cultivation.
There's a success story of a small-scale farmer who established an aquaponic system in their backyard. This enabled them to grow their own food sustainably while generating a surplus to sell locally. Not only did they enjoy fresh produce, mental and physical wellbeing, but they also experienced economic and environmental benefits. Insects and birds started visiting their backyard more frequently. From bees to hummingbirds the sheer amount of variety made exploring nature fun again.
Safe or Not for My Children and Me?
Aquaponics: Secure & Healthy for You & Kids!
Be assured: aquaponics is a safe way to get fish and veg for you and your little ones. Its closed-loop system gives plants nutrients from fish poo, reducing contamination risks.
This mix of aquaculture & hydroponics ensures no harmful chemicals are used like antibiotics or pesticides, making it a healthy choice. The controlled environment also minimizes water contamination, keeping you & your family safe. Another factor is the health benefits of cleaning and humidifying the air by plants. This can be very important in air polluted cities. Smog, exhaust fumes and carbon monoxide are filtered and exchanged for life essential oxygen. Further they can replace electricity intensive air conditioning in places like India or Thailand year round just by turning the sunlight into food and releasing water vapor into the air.
Plus, aquaponics promotes sustainable farming, eliminating overfishing worries. By cultivating fish in a controlled system, it reduces the need to capture fish from the wild with lots of unwanted bycatch like whales, dolphins or sea turtles, helping them survive in their natural habitats.
To make sure your aquaponic system is safe for your fam, there are a few tips. Regularly check water quality, like strange smell or fast breathing fish, to keep conditions optimal for plants & fish. Plus, maintain equipment & clean often to reduce any risks.
By following these pointers, you can enjoy aquaponics' eco-friendly & safe food production, while nourishing your family with fresh & healthy fish & veg!
Health and Aquaponics at Home
Health and aquaponics go hand in hand. When you have an aquaponics system in your home, you can grow fresh produce without chemicals or pesticides.
Here are some of the health benefits associated with home aquaponic systems:
- Fresh, Nutrient-Rich Produce: Aquaponics allows you to grow fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs year-round, providing a consistent source of nutrient-rich produce that is free from harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
- Antibiotic-Free Fish: Raising fish in a controlled environment reduces the risk of disease, eliminating the need for antibiotics and other chemicals. This results in healthier, antibiotic-free fish for consumption.
- Air Purification: Plants grown in aquaponic systems release oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to cleaner and fresher indoor air. They also have the ability to filter and purify the air by removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants.
- Increased Humidity: The evaporation of water from the aquaponic system can increase indoor humidity levels, which can be beneficial for respiratory health, skin hydration, and overall comfort, especially in dry climates or during winter months.
- Reduced Risk of Contaminated Produce: Growing your own produce reduces the risk of exposure to contaminated fruits and vegetables, which can sometimes occur in commercially grown products due to pesticide residues or bacterial contamination.
- Educational Value: Aquaponic systems offer educational opportunities for learning about ecosystems, plant growth, fish biology, and sustainable agriculture, fostering a greater understanding of food production and environmental stewardship.
- Promotes Healthy Eating: Having access to fresh produce and fish at home encourages healthier eating habits, promoting a balanced and nutritious diet.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly: Aquaponic systems use less water and land compared to traditional farming methods, contributing to sustainable food production and reducing the environmental footprint.
- Mental Wellbeing: Engaging with aquaponic systems can have therapeutic effects, reducing stress, promoting relaxation, and improving mental wellbeing. The presence of water and greenery can create a calming environment.
Sustainability of aquaponics: Feeding fish with plants, then the plants may end up as sushi! Crazy, right?
Sustainability of Aquaponics
Aquaponics: A Sustainable Combination of Aquaculture and Hydroponics.
This method recycles water from fish tanks, utilizes grey water to nourish plants, minimizes food waste by refeeding leftovers, enables individuals to produce food at home sustainably, reduces the need for agricultural land and deforestation, and provides a cost-effective protein source.
Knowing that you actively fight climate change can give you great purpose:
- Waste Repurposing: Aquaponic systems are excellent at turning waste into resources. Leftover food and organic kitchen waste can be introduced into the system as feed for fish and worms, contributing to a reduction in household waste and promoting a circular economy.
- No Microplastic Contamination: By growing your own produce and fish, you avoid the risk of microplastic contamination that can occur with commercially grown products due to the prevalence of single-use plastics in packaging and agricultural processes.
- Supporting Biodiversity at Home: Aquaponic systems create a balanced ecosystem within your home, supporting a variety of life including fish, plants, bacteria, and insects. This diversity contributes to the resilience and productivity of the system.
- Contributing to Wild Biodiversity: By relying less on commercially farmed produce and overfished stocks, you help reduce the pressure on natural ecosystems and contribute to the conservation of biodiversity in the wild.
- Reduced Use of Single-Use Plastics: Growing food at home reduces dependence on store-bought products that often come packaged in single-use plastics. This contributes to a reduction in plastic waste and helps prevent environmental contamination.
- Reduced Food Miles: Growing food at home reduces the need for transportation, lowering carbon emissions and ensuring fresher and more flavorful produce.
- No Synthetic Fertilizer and other Chemicals: Growing at home gives you a unique opportunity to have full transparency over your produce. This way you can ensure no harmful chemicals are used and no GMO is present.
Originating from ancient cultures, such as the Aztecs and Chinese, modern aquaponics combines technology with nature. Due to its eco-friendly approach and ability to address overfishing and land scarcity it is one of the most promising steps to become sustainable as individuals.
Do you want to start your own aquaponics system at home? Click on this step-by-step guide.
Short Summary
Aquaponics is a sustainable method of raising both fish and vegetables. It's a form of agriculture that combines raising fish in tanks (aquaculture) with soilless plant culture (hydroponics). In aquaponics, the nutrient-rich water from the fish tanks provides a natural fertilizer for the plants, which in turn help to purify the water in which the fish live.
The core of an aquaponics system is the aquaponics fish tank. Common fish used in aquaponics include tilapia, trout, catfish, and salmon, with tilapia being one of the most popular due to its resilience. Some adventurous practitioners even raise crawfish and shrimp! The choice of fish can depend on the local climate, regulations, and the system's goals, whether for consumption or ornamental purposes.
Water from the fish tank is pumped into plant growing areas, where plants uptake the nutrients. The types of plants that thrive in these systems range widely. Lettuce, herbs, and other leafy greens are especially common, but with the right setup, you can grow a variety of vegetables and even fruits. Some enthusiasts also experiment with vertical aquaponics or deep water culture variations to maximize their yield in small spaces.
Aquaponics setups can range from small DIY aquaponics systems, like mason jar aquaponics or mini aquaponics, to large commercial operations. One popular DIY method involves using IBC totes. Larger setups might be housed in specialized aquaponics greenhouses.
Comparing aquaponics vs hydroponics, the primary difference is the presence of fish. Hydroponics relies on added nutrients without the presence of fish. Another variant, aeroponics, mists the roots of the plants with nutrient-rich water. Each method has its pros and cons, but all aim to optimize growth conditions for plants.
There are various components to consider in an aquaponics system, from the type of grow media used to the water pumps, filters, and bell siphons that help regulate water flow. Designing an efficient system is crucial, whether you're aiming for a backyard aquaponics setup or a commercial-scale operation.
For beginners looking to delve into aquaponics, several starter kits and courses, like the aquaponics design course, provide step-by-step instructions. There are also numerous resources, such as books and forums, where enthusiasts share their designs, like the media bed aquaponics or the NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) aquaponics.
In summary, aquaponics is a promising, sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture and hydroponics. It offers benefits like reduced water usage and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, making it an eco-friendly option for modern agriculture.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
-
What is aquaponics? Aquaponics is a sustainable agriculture system that combines traditional aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) in a symbiotic environment.
-
How to set up an aquaponics system / How to build an aquaponics system? Setting up an aquaponics system involves preparing a fish tank, connecting it to plant grow beds, ensuring proper water circulation, and establishing a beneficial bacterial colony to convert fish waste into plant nutrients.
-
How to build an aquaponics greenhouse? An aquaponics greenhouse is a controlled environment that houses the aquaponics system. It involves constructing a transparent structure, ensuring temperature control, and setting up the aquaponics system inside to benefit from the controlled conditions.
-
How aquaponics works / How does aquaponics work / How does an aquaponics system work? Fish produce waste, which contains ammonia. Beneficial bacteria convert this ammonia into nitrates, which plants use as nutrients. As plants absorb these nutrients, they also clean the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tank.
-
Where to buy fish for aquaponics? / Where to buy fish for aquaponics system? / Where to buy fish for aquaponics near me? Fish for aquaponics can be purchased from local fish hatcheries, specialized aquaponics suppliers, or reputable online vendors.
-
What role do bacteria play in an aquaponics system? Beneficial bacteria are crucial in converting ammonia from fish waste into nitrates, which plants can absorb as nutrients.
-
What is the difference between hydroponics and aquaponics? Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without soil, while aquaponics combines aquaculture and hydroponics, using fish waste as a natural nutrient source for plants.
-
What can you grow with aquaponics? A variety of plants can be grown, from leafy greens like lettuce and herbs to larger plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, and even fruit trees, depending on the system's size.
-
What is the best fish for aquaponics / What fish are best for aquaponics / What are the best fish for aquaponics? Tilapia, catfish, and trout are commonly used because of their hardiness and growth rate. The choice often depends on local regulations and climate.
-
Why is aquaponics important? Aquaponics is a sustainable and efficient method of food production, using less water than traditional agriculture and eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers.
-
How to lower pH in aquaponics system / How to lower pH in aquaponics? pH can be lowered using natural methods like adding peat moss or certain organic acids. Monitoring and adjusting pH gradually is crucial.
-
How to make a bell siphon for aquaponics? A bell siphon is a self-regulating siphon mechanism for flood and drain systems. It involves an outer bell, an inner standpipe, and a media guard to ensure consistent water drainage.
-
How much does an aquaponics system cost? The cost varies depending on the system's size, materials used, and whether it's DIY or commercially purchased. Small DIY setups can start as low as $50, while larger commercial systems can run into thousands of dollars.
-
What to feed tilapia in aquaponics? Tilapia can be fed pellet fish food designed for them, supplemented with leafy greens or algae. Worms and black soldier fly larvae offer healthy protein and fats and can be bred at home.
-
Aquaponics how to build / How to start aquaponics / Aquaponics how to / How to do aquaponics / How to construct an aquaponics system pdf / How to set up aquaponics? Begin with understanding the space and resources available. Decide on the location, grow bed type, and what fish and plants you want to grow. Set up the fish tank, connect it to the grow beds, ensure proper water circulation, introduce fish, and then introduce plants.
-
How to make an aquaponics system / How to make a aquaponics system? Building an aquaponics system involves setting up a fish tank, creating grow beds (either floating or media-based), ensuring a water pump and filtration system, and establishing a healthy microbial community to aid in nutrient conversion.
-















.jpeg)
