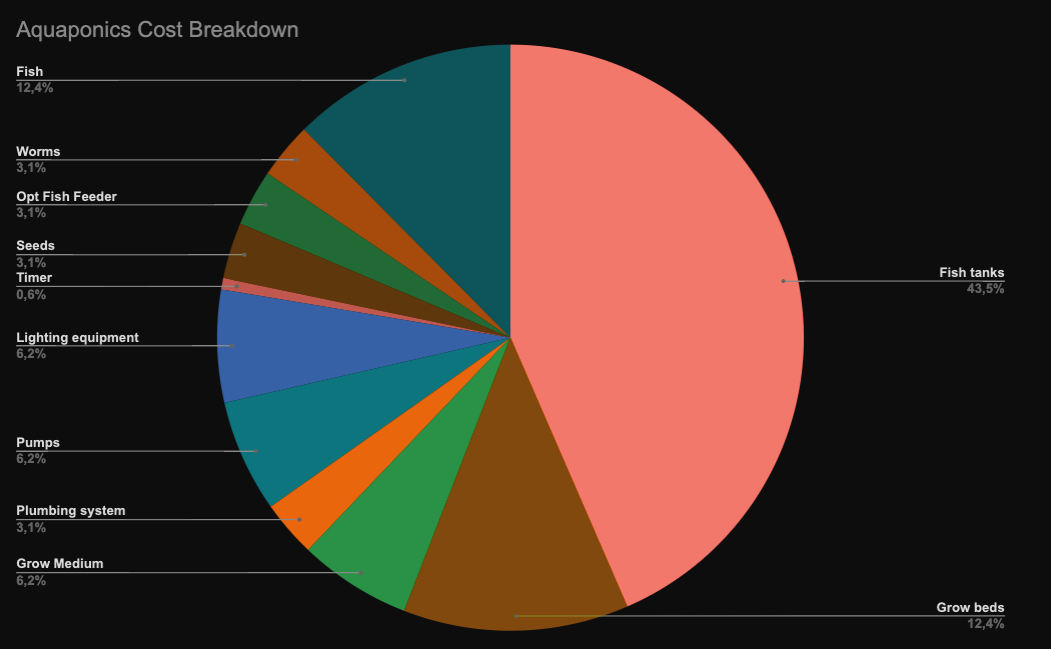
Considering choosing an Aquaponics Fish Tank but feeling lost about all the gear? No worries! This article will assist you in understanding the key points when picking the ideal fish tank for your aquaponics setup. Get ready to start growing healthy fish and plants!
Summary:
- Start with small DIY Systems to learn and adapt over time
- Choose non-toxic materials like glass, acrylic, or food-grade polyethylene.
- Avoid materials that can leach harmful substances, such as zinc, copper, and treated wood.
- Consider the balance between transparency and sturdiness for monitoring fish health.
Fish Tank Options for Aquaponics
Here are some popular choices of fish tanks for aquaponic enthusiasts:
Glass and Acrylic Aquariums
A favorite for indoor or small-scale setups, glass aquariums offer clarity, allowing for easy observation of fish and plants. Their sleek appearance is a plus, but they come with the risk of being breakable if not handled with care.
*As an Amazon Associate, I earn commission from qualifying purchases made through links in this post.*
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH | Price - September 2024 |
Price per Gallon
|
| Landen 45P 10 Gallon Rimless Low Iron Aquarium Fish Tank,W17.7×D11.8×H11.8 in(45x30x30cm) 5mm Thickness with Nano Foam Leveling Mat https://amzn.to/3C8FMQo |
10 Gallon 37 Liters |
18x12x12 inches 45x30x30 cm |
119.99$ | 11.99$ |
| LANDEN 90P 55 Gallon Rimless Low Iron Aquarium Tank,W35.4×D19.7×H19.7 in(90x50x50cm) 10mm Thickness with Black Nano Foam Leveling mat Included https://amzn.to/3AbPUr9 |
55 Gallon 208 Liters |
35x20x20 inches 90x50x50 cm |
529.99$ | 9.63$ |
| Landen 120P 72.2 Gallon Rimless Low Iron Aquarium Tank, W47.2 × D19.7 × H19.7 (120x50x50cm) 10mm Thickness with Black Nano Foam Leveling mat Included https://amzn.to/4hq5yjj |
72 Gallon 272 Liters |
47,2x19,7x19,7 inches 120x50x50 cm |
949.99$ | 13.19$ |
| LANDEN 150P 118.4 Gallon Rimless Low Iron Aquarium Tank, W59.1×D23.6×H21.7 in(150x60x55cm); 15 mm Thickness with Nano Foam Leveling Mat Included https://amzn.to/3Yr0thT |
118 Gallon 447Liters |
59x24x22 inches 150x60x55 cm |
1499.99$ | 12.71$ |
| 150 Gallon Starfire Glass Aquarium 60x24x24 12mm Eurobraced with Built-in Overflow Box https://amzn.to/3YpZpLn |
150 Gallon 568Liters |
60x24x24 inches 152x61x61 cm |
1795.00$ | 11.96$ |
Poly Tanks
These tanks, made of plastic, are budget-friendly and durable, perfect for aquaponic beginners. Their lightweight nature makes them easy to handle, and they're resilient to scratches and dents. The downside might be their susceptibility to discoloration, especially when exposed to direct sunlight.
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per Gallon
|
| Fortex-Fortiflex 2401101DP Stock Tank https://amzn.to/4e5jht3 |
110 Gallon 416 Liters |
10x10x10 inches 25.4x25.4x25.4cm |
271.67$ | 2.47$ |
| ENPAC Extra Large Tote Bin, Yellow, 223 Gallon, Durable, UV Resistant, 100% Polyethylene, Nestable, Forkliftable https://amzn.to/4eciEOm |
223 Gallon 844 Liters |
51.5x47.25x33 inches 130.8x120x83.8 cm |
285.00$ | 1.28$ |
| ENPAC Poly Tank Containment Sump, Black, 275-Gallon, Durable Polyethylene, Saves Space https://amzn.to/3Ank8r0 |
275 Gallon 1041 Liters |
82x45x35.5 inches 208.3x114.3x90.2 cm |
860.00$ | 3.13$ |
| Enpac IBC Tote Space-Saver Spill Pallet, Drain, Yellow, Durable, Rugged Design, Narrow Footprint, Removable Platform https://amzn.to/3NPBGPU |
275 Gallon 1041 Liters |
57x57x47 inches 143x143x119.4cm |
1845.00$ | 6.71$ |
| Enpac IBC Tote Cross-Contain Spill Pallet, Sump Only, Black, Polyethylene, 4-way Forkliftable, Nestable Stacking, 385 Gallon Spill Capacity https://amzn.to/3YMrQ7J |
385 Gallon 1457 Liters |
79x78x20 inches 200.7x198.1x50.8 cm |
656.00$ | 1.70$ |
| Black Diamond 5469-BD IBC Containment Pallet https://amzn.to/3YsdAiU |
385 Gallon 1457 Liters |
81x73x30 inches 206x185x76cm |
1600.00$ | 4.16$ |
| ENPAC Poly Tank Containment Sump, Black, 550-Gallon, Durable Polyethylene, Saves Space, Large Interior https://amzn.to/4fsMZt2 |
550 Gallon 2082 Liters |
113x71x32 inches 287x180.3x81.3 cm |
1367.00$ | 2.49$ |
| 82124749 Polyethylene Vertical Reservoir Water Tank, 550 Gallon, Made in The USA, Poly Tank for Water and Non-Flammable Liquids, Rust and Corrosion Proof https://amzn.to/4f4olyV |
550 Gallon 2082 Liters |
67x67x45 inches 173x173x114 cm |
1004.84$ | 1.83$ |
| Horizontal with Legs Water Tank, 550 Gallon, White https://amzn.to/4hu7ozB |
550 Gallon 2082 Liters |
78x48x49 inches 198x121x124 cm |
1002.99$ | 1.82$ |
| Tarter, Big Blue Poly Round Tank, 8ft.x2ft., Model# WTP82 https://amzn.to/4hvFRh4 |
625 Gallon 2366 Liters |
96x96x24 inches 244x244x61 cm |
674.92$ | 1.08$ |
| Enpac Double IBC Tote Spill Pallet XL, Drain, Yellow, UV Resistant, Polyethylene, Forkliftable, Removable Platform https://amzn.to/40sZNLF |
750 Gallon 2839 Liters |
113x71x32 inches 287x180.3x81.3 cm |
3723.00$ | 4.96$ |
| Enpac Double IBC Tote Spill Pallet XL, Yellow, UV Resistant, Polyethylene, Forkliftable, Removable Platform https://amzn.to/4hryuaE |
750 Gallon 2839 Liters |
113x71x32 inches 287x180.3x81.3 cm |
3667.00$ | 4.89$ |
Rubbermaid Farm Tanks
Constructed from robust plastic designed for agricultural use, Rubbermaid farm tanks are built for durability. They can accommodate larger aquaponic systems due to their vast volume capacity. The opaque nature of these tanks, however, makes visual monitoring a bit tricky.
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per Gallon
|
| Rubbermaid Commercial Products Stock Tank, 50-Gallons, Structural Foam, Heavy Duty Container, for Livestock/Animal/Cattle Feed & Water, Outdoor Homemade Pool/Hot Tub/Bathtub, & Pet Cleaning/Dog Wash https://amzn.to/3AmvzPK |
50 Gallon 189 Liters |
51x31x12 inches 130x78x30 cm |
100.99$ | 2.02$ |
| Rubbermaid Commercial Products Stock Tank, 70-Gallons, Structural Foam, Heavy Duty Container, for Livestock/Animal/Cattle Feed & Water, Outdoor Homemade Pool/Hot Tub/Bathtub, & Pet Cleaning/Dog Wash https://amzn.to/3Uw3JY8 |
70 Gallon 265 Liters |
32x30.5x24 inches 81x77.5x61 cm |
204.99$ | 2.93$ |
| Rubbermaid Commercial Products Stock Tank, 100-Gallons, Structural Foam, Heavy Duty Container, for Livestock/Animal/Cattle Feed & Water, Outdoor Homemade Pool/Hot Tub/Bathtub, & Pet Cleaning/Dog Wash https://amzn.to/3YKlAwW |
100 Gallon 378 Liters |
53x31x25 inches 135x78x63 cm |
299.99$ | 3.00$ |
| 150 Gallon STOCK TANK https://amzn.to/4f39sNt |
150 Gallons 567 Liters |
58x39x24.5 inches 147x99x62 cm |
314.99$ | 2.10$ |
| Rubbermaid Commercial Products Stock Tank, 300-Gallons, Structural Foam, Heavy Duty Container, for Livestock/Animal/Cattle Feed & Water, Outdoor Homemade Pool/Hot Tub/Bathtub, & Pet Cleaning/Dog Wash https://amzn.to/3C8GyNi |
300 Gallon 1135 Liters |
63x69x25 inches 160x175x63 cm |
499.99$ | 1.67$ |
IBC Containers
Common in the industrial sector for liquid storage and transport, IBC containers are a robust and cost-effective choice for aquaponics. Their tough build ensures longevity, but like the Rubbermaid tanks, their non-transparent nature can pose challenges for visual inspections.
Best Bang per Buck: Used / Refurbished IBC Container in your area
*As an eBay Affiliate, I earn commission from qualifying purchases made through links in this post.*
| Product | Link | Price ($) | Capacity (Gallons/ Liter) | Price per Gallon ($) | Location |
| 275 Gallon IBC Tote - Water Tank | https://ebay.us/l3FSAU | 100.00$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.36$ | New York |
| 275 Gallon IBC Tote - Water Tank | https://ebay.us/fGD7Tr | 99.00$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.36$ | California |
| 275 Gallon IBC Tote - Water Tank - CONTACT FOR SHIPPING QUOTES | https://ebay.us/Zr35Pd | 150.00$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.55$ | Pennsylvania |
| USED 275 Gallon IBC Tote / Fluid Container Schuetz IBC275GAL | https://ebay.us/j75gKx | 99.00$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.36$ | California |
| IBC Tote Cove, 275 Gallon IBC Water Storage Barrel Liner Bags | https://ebay.us/VRXcC0 | 122.99$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.45$ | Florida |
| IBC Tote Cove, 275 Gallon IBC Water Storage Barrel Liner Bags | https://ebay.us/FCgmdS | 73.09$ | 275 Gallons/ 1040 Liter | 0.27$ | Alabama |
| 330 Gallon IBC Tote Tank | https://ebay.us/Cs8AOU | 250.00$ | 330 Gallons/ 1250 Liter | 0.76$ | Ohio |
New IBC Container:
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per Gallon
|
| 275 Gallon IBC Tote with Metal Pallet & Cage https://amzn.to/4eciV3Q |
275 Gallon 1040 Liters |
47.5x39.5x45.5 inches 120x100x115 cm |
621.22$ | 2.26$ |
| Global Industrial IBC Container 275 Gallon UN Approved w/Composite Metal Pallet Base https://amzn.to/3Uxv0cZ |
275 Gallon 1040 Liters |
47.5x39.5x45.5 inches 120x100x115 cm |
730.13$ | 2.66$ |
| IBC Tank 330 Gallon for Water or Liquid Storage and Dispensing, HDPE Tank Surrounded by a Galvanized Steel cage https://amzn.to/3NMqxz1 |
330 Gallon 1250 Liters |
48x40x53 inches 122x102x134 cm |
1450.00$ | 4.39$ |
Above Ground Fish Pond
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per Gallon
|
| Canvas Fish Pond, Fish Show Water Tank with Stainless Steel Tubes, Foldable Water Storage Pond, Aquarium Ornamental Swimming Pool with Drain Valve, Temporary Holding Viewing Canvas Fish Pond https://amzn.to/3UxQjLo |
127 Gallon 480 Liters |
47.2x31.4x19.6 inches 119.9x79.8x49.8 cm |
230.00$ | 1.81$ |
| WANLIAN Pool Above Ground Canvas Fish Pond Circular Thickening Pool Large Collapsible Outdoors Tarpaulin for Koi Culture Agricultural Irrigation Water Storage Tank,Easy to Install(Belt Frame)(3 * 1) https://amzn.to/4f6nsWK |
1849 Gallon 7000 Liters |
117.6x117.6x38.4 inches 298.7x298.7x97.5 cm |
629.00$ | 0.34$ |
| Lily Clear View Garden Aquarium - Raised Hexagon Pond (Light Grey) https://amzn.to/4f4Miq5 |
145 Gallon 549 Liters |
66.93x57.87x20.08 inches 170x147x51 cm |
1350.00$ | 9.31$ |
Swimming Pool and Other
Large amount of water volume for small money, but it won't last as long as the other options.
| Product | Volume | Measures LxWxH |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per Gallon
|
| INTEX 28205EH Metal Frame Above Ground Swimming Pool: 8ft x 20in – Puncture-Resistant Material – Easy Assemble – Rust Resistant – 483 Gallon Capacity https://amzn.to/4e8R8kK |
483 Gallons 1828 Liters |
96x96x20 inches 244x244x50.8 cm |
96.99$ | 0.20$ |
| Metal Pro 8'3" X 5' X 26" Rectangle Pool Durable Steel Frame Above Ground Pool for Outdoor Backyard Swimming Pool Suitable Friends Family Adults Kids https://amzn.to/4f4MtBL |
500 Gallons 1893 Liters |
99x60x25 inches 251.4x152.4x63.5 cm |
142.99$ | 0.28$ |
| Bestway Steel Pro 9.8' x 6.6' x 26" Rectangular Steel Frame Above Ground Outdoor Backyard Swimming Pool Set with 330 GPH Filter Pump https://amzn.to/48wTQ2d |
827 Gallons 3130 Liters |
117.6x79.2x26 inches 298.7x201.2x66 cm |
184.99$ | 0.22$ |
| Bestway Power Steel 14’ x 42” Round Above Ground Outdoor Backyard Swimming Pool Set with 1,000 GPH Filter Pump, Ladder, and Pool Cover https://amzn.to/48LH8Nr |
2941 Gallons 11133 Liters |
42x42x14 inches 106.7x106.7x35.6 cm |
429.99$ | 0.15$ |
| Intex 26325EH Ultra XTR Deluxe Above Ground Swimming Pool Set: 16ft x 48in – Includes 1500 GPH Cartridge Sand Filter Pump – SuperTough Puncture Resistant – Rust Resistant – Easy to Assemble https://amzn.to/48t06rE |
5061 Gallons 19158 Liters |
192x192x48 inches 487x487x121.9 cm |
799.94$ | 0.16$ |
| Intex Ultra XTR Deluxe Above Ground Swimming Pool Set, Includes Cartridge Sand Filter Pump, SuperTough Puncture Resistant, Rust Resistant, 26' x 52" https://amzn.to/3NOQtKA |
14667 Gallons 55521 Liters |
312x312x52 inches 792.5x792.5x132 cm |
1499.99$ | 0.10$ |
| Intex 26355EH Ultra XTR Deluxe Rectangular Above Ground Swimming Pool Set: 18ft x 9ft x 52in – Includes 1500 GPH Sand Filter Pump – SuperTough Puncture Resistant – Rust Resistant – Easy to Assemble https://amzn.to/3YuW8u9 |
4545 Gallons 17204 Liters |
216x108x52 inches 549x275x132 cm |
1181.69$ | 0.26$ |
| INTEX 26373EH Ultra XTR Deluxe Rectangular Above Ground Swimming Pool Set: 32ft x 16ft x 52in – Includes 2800 GPH Sand Filter Pump – Easy Assembly https://amzn.to/4fsfrLv |
14364 Gallons 54373 Liters |
384x192x52 inches 975x487x132 cm |
1789.99$ | 0.12$ |
Pond Liners
Instead of buying a premade fish tank, you can also use old structures like fridges, bathtubs, big containers, or other stable structures and seal them with pond liners. These are also perfect for building your own construction out of wood or metal, perfectly fitting your area and needs and waterproofing it.
| Product | Thickness | Measures LxW |
Price - September 2024
|
Price per square Feet
|
| KLEWEE Pond Liner, 4 x 7ft 20 Mil Small Pond Liners, Black Heavy LDPE Duty Pond Liners for Outdoor Ponds, Waterfall, Stream, Fountains https://amzn.to/3NPSPIY |
20 Mil | 84x48 inches 213.3x121.9 cm |
15.95$ | 0.57$ |
| 10 x 13 Feet Pond Liner, 20 Mil Pond Liners for Outdoor Ponds, Black LDPE Pond Liner for Waterfall, Fish Koi Ponds, Garden Fountain https://amzn.to/3UxQnL8 |
20 Mil | 156x120 inches 396.2x304.8 cm |
34.99$ | 0.27$ |
| yeezoo 30X30FT Reinforced Large PE Pond Liner, KOI Pond Liners for Outdoor Ponds, Enhanced 5-Layer Structure Pond Liner for Fish, Duck, Garden Raised Bed and Waterscape Pond(0.82oz/sq ft Thickness) https://amzn.to/3NK83PU |
0.82oz/sq ft | 360x360 inches 914x914 cm |
239.99$ | 0.27$ |
| Firestone 45mil EPDM Rubber Pond Liner 15ft.x20ft. https://amzn.to/4foY5iC |
45 Mil | 180x240 inches 457x610 cm |
338.00$ | 1.13$ |
| LifeGuard Pond Liner 15 ft. x 200 ft. 45 Mil EPDM Rubber - LG15X200-45 https://amzn.to/3AjKsm0 |
45 Mil | 180x2400 inches 457x6096 cm |
3534.00$ | 1.18$ |
| LifeGuard Pond Liner 30 ft. x 200 ft. 45 Mil EPDM Rubber - LG30X200-45 https://amzn.to/3YKsVN9 |
45 Mil | 360x2400 inches 914x6096 cm |
7068.00$ | 1.18$ |
| LifeGuard Pond Liner 25 ft. x 100 ft. 60 Mil EPDM Rubber - LG25X100-60 https://amzn.to/3YJ01Nk |
60 Mil | 300x1200 inches 762x3048 cm |
3625.00$ | 1.45$ |
Size and How it Affects Aquaponics System
Size is a major factor that heavily influences the performance of an aquaponics system. Tank size affects stock density, water quality, and productivity. Let's look at the connection between tank size and its effects on different parts of an aquaponics system.
See the table below for the correlation between tank size and its effects:
|
Tank Size |
Stock Density |
Water Quality |
Productivity |
|
Small |
Low |
Maintainable, but prone to fluctuations |
Limited |
|
Medium |
Moderate |
Balanced with proper maintenance |
Balanced |
|
Large |
High |
Less susceptible to changes |
High |
Smaller tanks allow for lower stock density, meaning fewer fish. This results in faster growth rates of individual fish but less harvest. Small tanks are more accessible so are easier to maintain, but the water quality fluctuates more.
Larger tanks enable higher stock densities for more harvest or low stock densities for faster growth. Maintaining water quality is easier due to having more water that dilutes the toxins like ammonia or nitrite. Optimal conditions for both plant and fish health can be achieved with size adjusted grow beds.
These findings give us important insights into tank sizing considerations. Choosing the right size will maximize productivity while avoiding issues associated with undersized or oversized tanks. Even though oversized is not really a problem as you can just add more fish to compensate.
To reap the rewards of a well-designed aquaponics fish tank that fits your needs, make sure to carefully select a suitable size taking these factors into account. A balanced tank size ensures harmony between fish and plant growth, leading to a thriving aquaponics system.
Recommended Height of an Aquaponics Fish Tank
Aquaponics Fish Tank Height: Finding the Perfect Dimensions
When selecting an aquaponics fish tank, height is an important factor. The suggested height of an aquaponics fish tank varies depending on the type of fish or shrimp. Shrimp don't mind the height, however, some species have definite needs. Generally, a tank with a height of 1 to 2 feet is sufficient for most types of fish.
For example, here are the recommended heights of different types of fish:
|
Fish Type |
Recommended Height (in feet) |
|
Tilapia |
1-2 |
|
Salmon |
2-3 |
|
Catfish |
1-2 |
|
Trout |
2-3 |
It is important to remember that these recommendations should be evaluated together with other factors like water volume and surface area. Adding floors can be a good idea if you need more space for shrimp or other bottom-dwelling species.
Apart from tank height, you should also take other conditions into consideration such as water quality, temperature, and oxygen levels. This will ensure both plants and fish have a healthy environment.
Did you know? Research from aquaponics experts shows that having the right water conditions in an aquaponics system results in better health and faster growth of plants and fish.
To make sure your fish won't jump out of the tank, the floor area needs to be big enough for the size of the tank and your fish.
Floor Area for Your Fish
Floor area in an aquaponics system is essential for your aquatic inhabitants. It affects their health and well-being. Providing ample space creates a sustainable living environment.
To understand floor area better, let's look at some key factors:
|
Factors |
Importance |
|
More swim area |
High |
|
More water volume |
High |
|
More height |
Low |
|
More potential grow area |
Medium |
|
More sunlight |
Low |
This helps determine the ideal floor area. Allocating more swim area lets the fish exercise and move, promoting their health and offering them the best life possible. A larger potential grow area may create a more balanced ecosystem for you.
Sunlight is also important. It provides nutrients like algae as food and vitamin D in fish and supports optimal water temperature.
A story of an aquaponics enthusiast who didn't provide enough floor area and sunlight shows why it's so crucial. Their fish became stressed and didn't grow. They modified their setup and saw instant improvements in the well-being of their fish.
Therefore, when choosing an aquaponics fish tank, consider floor area to ensure the success of your aquatic companions. The shape is also important - no one wants a boring fish bowl!
How The Shape of Your Fish Tank Influences The Fish
The shape of your fish tank has a huge effect on the health and behavior of your aquatic pets. Here are four noteworthy points to keep in mind:
- A square-shaped tank offers plenty of swimming room, letting the fish move around freely and act naturally.
- An oval-shaped tank encourages good water flow, so all parts of the tank get oxygen and nutrients.
- A round fish tank takes away the fish's stress as there are no corners they can feel trapped in.
- The shape of the tank can also influence filtration efficiency. For example round shaped tanks provide better zones filtering inlets as all dirt flows to the middle where your pump should be.
When selecting a fish tank shape, consider other factors too. Think about the needs and habits of the fish species and whether the tank fits in with the rest of your aquaponics setup.
To make sure your aquatic pets are safe and happy, consider these tips:
- Find out more about your chosen fish species and how the tank shape could suit their needs.
- Don’t overcomplicate, cause the shape does not matter that much and every shape will work just fine.
- If you use a grow bed pump system, make sure the tank shape makes it easy to install and manage the grow bed if you plan to put it on top of the tank.
By following these tips, you can choose a fish tank shape that looks great and provides the perfect habitat for your aquatic friends. And remember, choose a fish tank in accordance with your location - fish don't like long commutes either!
Are you looking for a full step-by-step guide for an Automated Aquaponics System? Click here.
Type of Fish Tank Depends on Location
Choosing a fish tank for aquaponics depends on the location. Different places have varied requirements. For instance, greenhouses often use glass or polycarbonate tanks for maximum light and heat. Outdoors or in a garage, fiberglass or plastic is preferable to protect from the elements. Plus, bear in mind the size of the tank - bigger ones need extra room and support. Remember, glass or polycarbonate is usually used inside your home to watch your fish. And don't forget, you don't need to be extravagant - unless your fish are secretly goldfish influencers!
Price And Budget of an Aquaponics Fish Tank
Analyzing the Price and Budget of an Aquaponics Fish Tank requires considering various factors such as tank size, materials, and additional equipment. Carefully assessing these aspects helps to find the most cost-effective options with the best return on investment.
The table below outlines the different price ranges for aquaponics fish tanks based on size and material:
|
Tank Size |
Material |
Price Range ($) |
|
Small |
Plastic |
50 - 100 |
|
Medium |
Glas / Plastic |
200 - 500 |
|
Large |
Concrete |
1000 - 5000 |
It is important to note that the prices are approximate and can vary. Maintenance costs must also be taken into account when evaluating the overall budget.
Sustainability also plays a role when choosing an aquaponics fish tank. Opting for tanks made from recycled or eco-friendly materials reduces costs and aligns with environmental values. IBC Containers for example can be bought cheap from local producers and if used for food are also food safe.
If you go for an indoor set up make sure to invest in a solid option as leaks will become really expensive really quick.
John's story is an example. He bought the cheapest fish tank in his area, but soon realized it had frequent leaks and water quality issues due to poor plastic quality materials.
Considering both price and budget when selecting an aquaponics fish tank will lead to a sustainable and profitable investment. A solid foundation for the fish tank is essential, unless you want your aquatic pets to take part in a shore leave routine!
Structural Integrity Of The Ground On Aquaponics Fish Tanks
Stability of the ground below an aquaponics fish tank is key for its integrity. It needs to support the weight of the tank, water and fish. Ensure the ground is strong and stable to avoid any damage or tank collapse.
To ensure the ground is able to hold the aquaponics fish tank, assess the buildings load-bearing capacity. Do this via testing or consult a professional engineer or geotechnical specialist. They will determine if the ground can withstand the weight and advise on any modifications.
If the assessment shows the ground cannot support the tank, make it smaller or reduce water. Alternatively, install beams or columns to distribute the weight over a wider area.
Additionally, keep the tank ground surface flat to avoid stress points or instability.
Choosing the right materials for your aquaponics fish tank is a must. A sturdy tank means less chance of fish going for a walk.
Material Choices When Building an Aquaponics Fish Tank
When I first delved into aquaponics, the abundance of options and considerations was overwhelming, but the journey of setting up my first tank was both enlightening and rewarding. I learned the intricacies of balancing tank size with stock density and the importance of choosing the right materials to ensure the well-being of my aquatic inhabitants.
Building an aquaponics fish tank requires careful consideration of the materials used. The ideal material should be non-toxic, waterproof, sturdy, and, in some cases, transparent to observe the fish and monitor their health. Here, we will explore various material options and their properties to help you make an informed decision for your aquaponics system.
1. Toxicity
Here is a list of materials you should avoid due to potential harmful leaching, along with a list of safe alternatives for building an aquaponics fish tank:
Materials to Avoid:
- Zinc: Zinc can be toxic to fish and can leach into the water, especially in a corrosive environment.
- Copper: Copper pipes and containers can leach copper ions, which can be harmful to fish and plants.
- Lead: Old lead-based paints and pipes should be avoided as lead is toxic to both fish and plants.
- Treated Wood: Wood treated with pesticides, fungicides, or other chemicals can leach toxins into the water.
- Galvanized Metal: Galvanized materials contain a zinc layer which can leach into the water.
- Unsealed Concrete: Concrete can leach lime into the water, raising the pH to harmful levels if not properly sealed.
- PVC with Phthalates: Some PVC materials contain harmful phthalates, so it's essential to choose food-grade or safe PVC.
- Non-Aquarium Safe Sealants: Some sealants can leach harmful chemicals, so only use those labeled as safe for aquariums.
Safe Material Options:
- Food-Grade Polyethylene: This plastic is commonly used for water storage and is safe for fish and plants.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass tanks are sturdy and safe for aquaponics, but ensure the resin used is also safe.
- Glass: Glass is a non-toxic and transparent option, especially useful for smaller tanks.
- Acrylic: Acrylic is a transparent plastic material that is lighter and more impact-resistant than glass.
- Food-Grade or Aquaponic-Safe PVC: Ensure the PVC is free of phthalates and is rated as safe for food or aquaponics.
- EPDM Pond Liner: EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a type of rubber pond liner that is safe for fish.
- Aquarium-Safe Sealants: Use sealants that are labeled as safe for aquarium use to prevent harmful leaching.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): HDPE is a safe plastic material for constructing fish tanks and grow beds.
When selecting waterproof materials, sealants, and coatings for an aquaponics fish tank, it is essential to ensure that the products are non-toxic and safe for both fish and plants. By using appropriate materials, you can ensure no harmful chemicals are in your food.
2. Waterproofing
Waterproof materials are essential for holding water and preventing leaks.
here's a list of waterproof materials, sealants, and coatings that are commonly used in various applications, including aquaponics:
Waterproof Material Options:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Commonly used for water storage tanks.
- Food-grade PE is safe for aquaponics.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Sturdy and safe plastic material for constructing tanks and grow beds.
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Resistant to chemicals and can be used as a container material.
- Fiberglass
- Composed of reinforced plastic and glass fibers.
- Ensure the resin used is safe for aquaponics.
- Glass
- Non-toxic and commonly used for aquariums.
- Acrylic
- Transparent plastic material that is lighter and more impact-resistant than glass.
- EPDM Pond Liner
- Rubber liner safe for fish and commonly used for ponds.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- Ensure it is food-grade or aquaponics-safe.
Sealants:
- Aquarium Silicone Sealant
- Clear, waterproof, and safe for fish and plants.
- Commonly used for sealing glass aquariums.
- Marine Epoxy
- Waterproof and used for a variety of applications including sealing tanks.
- Polyurethane Sealant
- Waterproof and flexible sealant.
- Teflon Tape
- Used for sealing pipe threads.
- Plumbers' Putty
- Waterproof and used for sealing plumbing applications.
Coatings:
- Pond Shield Epoxy
- Non-toxic epoxy coating used for sealing concrete ponds and tanks.
- Rubberized Coatings
- Flexible and waterproof, used for a variety of applications.
- Liquid Rubber
- Waterproof coating commonly used for roofs, but can also be used for tanks.
- Aquaponics Liner
- Specialized liner used to waterproof the interior of aquaponics systems.
3. Sturdiness
Ensuring the sturdiness of your aquaponics fish tank is pivotal, as it will be tasked with holding not only a significant weight of water but also living organisms, such as fish and plants. Here’s a closer look at some of the key considerations regarding the sturdiness of an aquaponics fish tank.
1. Structural Integrity:
- Structural integrity is a critical factor in the design and construction of aquaponics fish tanks. A tank with high structural integrity can withstand the pressures exerted by the water and the movement of fish, reducing the risk of leaks and breakages.
-
Importance: A sturdy tank prevents accidents, ensures the safety of the living organisms inside, and prolongs the lifespan of the aquaponics system.
-
Considerations: The tank’s design, material thickness, and quality all contribute to its structural integrity.
2. Material Strength:
Different materials come with varying levels of strength and durability. Here are a few common materials used in aquaponics fish tanks and their comparative strengths:
-
Glass: Glass tanks are popular due to their transparency and aesthetic appeal. However, they are heavy and prone to breakage, especially if not adequately supported.
-
Acrylic: Acrylic is lighter and 17 times more impact-resistant than glass, making it a safer alternative. However, it can scratch easily.
-
Concrete: Concrete tanks are exceptionally sturdy and durable but are permanent and not transparent. They are suitable for large-scale aquaponics systems.
-
Polyethylene: Polyethylene tanks are lightweight, durable, and resistant to impact. They are versatile and suitable for various scales of aquaponics systems.
3. Reinforcement Techniques:
Enhancing the sturdiness of your fish tank can be achieved through several reinforcement techniques:
- Frames and Supports: Using metal or wooden frames can provide additional support to the tank, especially for glass and acrylic tanks.
-
Thickness of Material: Opting for materials with greater thickness can enhance the strength and durability of the tank.
-
Foundation Stability: Ensuring that the tank is placed on a stable and level foundation can prevent uneven pressure distribution and potential structural issues.
-
External Bracing: Adding external braces to the tank can help distribute the load and improve the overall structural integrity.
Sturdiness is paramount in constructing a reliable and safe aquaponics fish tank. Considering the structural integrity, choosing materials with the right balance of strength and other attributes, and employing reinforcement techniques are all essential steps in building a tank that will stand the test of time and prevent a total economic loss.
4. Transparency
Transparency in an aquaponics fish tank offers the dual benefit of aesthetic appeal and practical functionality. It enables growers to monitor the well-being of the fish and observe the ecosystem's dynamics. Here, we will delve into the significance of transparency, evaluate material options, and explore how to strike a balance between transparency and strength.
1. Benefits for Monitoring:
Having a transparent fish tank in an aquaponics system offers several monitoring advantages:
-
Observing Fish Behavior: Transparent tanks allow for easy observation of fish behavior, which is essential for detecting signs of stress, disease, or abnormal activity.
-
Health Monitoring: Regular visual checks on fish health become feasible, enabling timely intervention if issues arise.
-
System Check: Transparency aids in quickly assessing water clarity, detecting algae growth, and ensuring that the system components are functioning correctly.
2. Transparent Material Options:
Several transparent materials are available, each with its unique properties:
-
Glass: Glass is a popular choice due to its excellent clarity and aesthetic appeal. It is, however, heavier and more prone to breakage compared to acrylic.
-
Clear Acrylic: Acrylic offers superior impact resistance, is lighter than glass, and maintains clarity over time. It can, however, scratch more easily than glass.
3. Balancing Transparency and Strength:
While transparency is valuable for monitoring, it is crucial to balance it with the tank’s structural integrity:
-
Material Thickness: Opt for thicker glass or acrylic to enhance strength without compromising transparency.
-
Reinforcement: Employing frames, supports, or bracing can reinforce the tank structure while retaining the viewing advantage.
-
Partial Transparency: Consider designs that incorporate transparent viewing panels within a sturdier, non-transparent structure, achieving a balance between observation and strength.
Transparency in an aquaponics fish tank serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. Choosing the right transparent material and thoughtfully balancing transparency with structural strength will lead to a more successful and enjoyable aquaponics experience.
5. Additional Considerations
- UV Resistance: Consider materials that resist UV degradation for outdoor tanks exposed to sunlight.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Examine materials that can withstand big temperature fluctuation, especially for outdoor systems.
- Cost and Availability: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and availability of different materials in your region.
Location is key when it comes to growing beds for fish. The wrong spot could lead to unhappy tenants - or even an underwater revolt!
Grow Bed Location of Your Aquaponics System
For safety, always ensure that the grow bed is positioned above the water line. This way, if there are issues like pump failure, plumbing problems, or power outages, it prevents a reverse siphon effect that could drain all the water from the tank.
Weight & Size: Look at the size and weight of your grow bed before you decide where to place it. Make sure wherever you pick can support the weight of the filled bed without any risk of collapsing.
Proximity to Water: Positioning the bed close to a source of water makes filling and maintenance easier. It also limits the need for long pipes, reducing the likelihood of leaks.
Vertical Farming: Vertical farming uses space efficiently by stacking beds. Consider the height of your setup to get the most out of it.
Gravity Sand Filter Bed: An aquaponics system with a gravity sand filter needs the grow bed to be placed above the fish tank. This will make sure water flows through the sand filter first, keeping the tank clean and free from solids.
When planning an aquaponics system, keep safety and efficiency in mind. Consider size, proximity to water, vertical farming methods, and positioning the bed above the fish tank. Start growing your own sustainable produce today!
Harvest Goals for Your Size of Fish Tank
Harvesting yields depend on the size of your aquaponics fish tank. To maximize productivity, set goals based on tank capacity and fish-to-plant ratios.
Harvest Goals for Your Size of Fish Tank per Month:
| Tank Size (Gallons/Liters) | Fish Quantity (lbs/kg) | Plant Yield (lbs/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 26 Gallon / 100 Liter | 2.6 lbs / 1.18 kg | 3.5 lbs / 1.59 kg |
| 75 Gallon / 283 Liter | 7.5 lbs / 3.4 kg | 10 lbs / 4.54 kg |
| 100 Gallon / 378 Liter | 10 lbs / 4.54 kg | 13.3 lbs / 6.03 kg |
| 150 Gallon / 568 Liter | 15 lbs / 6.8 kg | 20 lbs / 9.07 kg |
| 200 Gallon / 756 Liter | 20 lbs / 9.07 kg | 26.6 lbs / 12.07 kg |
| 300 Gallon / 1136 Liter | 30 lbs / 13.6 kg | 40 lbs / 18.14 kg |
| 500 Gallon / 1893 Liter | 50 lbs / 22.68 kg | 66.6 lbs / 30.2 kg |
For a 75-gallon tank, 7.5 pounds of fish yields about 10 pounds of plants. It's important for the plants to grow in proportion to the amount of fish in the tank. This happens naturally as seedlings need less nutrients than big plants and ensures nutrients are used efficiently.
Consider having more plants than necessary. This promotes healthier fish growth and acts as a safeguard for any issues.
Maximize the potential of your aquaponics system with the right harvest goals and a balanced system. Superior results come from managing both fish and plant growth effectively. Why not put your fish tank in the living room and get a tan while hanging out with your aquatic friends?
Sunlight and Fish Tanks
Sunlight is vital for aquaponics fish tanks. It gives plants energy to do photosynthesis, which filters the water and takes out ammonia and nitrates made by fish waste. Sunlight and water always produces algae, a natural water filter and a great protein and omega 3 source for the fish. Also, sunlight helps fish to make Vitamin D, grows them healthier, and strengthens their immune system.
|
Sunlight Exposure |
Benefits |
|
Adequate sunlight |
Helps plants grow, filters water, and assists Vitamin D synthesis in fish, algae for extra food and water filter |
|
Not enough sunlight |
Plants might not grow, filter doesn't work well, and fish may lack Vitamin D, can add light through LEDs |
|
Too much sunlight |
May cause high water temperature |
It is important to give the fish tank intense sunlight and harvest this free natural energy as much as possible. The water temperature must be taken into account.
To benefit from sunlight in your aquaponics system:
- Place the tank where it can get enough sunlight.
- Use awnings or curtains if you notice too high water temperature.
- Keep track of the nutrients, especially nitrogen, because algae and plants compete for the same fertilizer.
By understanding and managing sunlight, you can give your plants a healthy environment and keep optimal conditions for your fish.
Transform that old bathtub into an awesome fish tank and watch your aquatic friends swim with style while you think of other household items to repurpose!
DIY Repurpose For Aquaponics Fish Tank
Using DIY techniques, aquaponics fish tanks can be repurposed. Various containers like ponds, pools, IBC containers, aquariums, rain collection tanks, rain barrels, and even bathtubs can be used. These containers offer a sustainable way to create productive aquaponics systems.
I remember transforming an old bathtub into a thriving ecosystem, witnessing the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants unfold before my eyes. The experience was not only sustainable but also a creative testament to repurposing everyday items.
The table below gives a breakdown of the options:
|
Container Type |
Description |
|
Pond |
Large outdoor water bodies for aquaponics. |
|
Pool |
Swimming pools can be transformed into aquaponic systems. |
|
IBC |
Cost-effective for indoor small-scale farming. |
|
Aquarium |
Suitable for smaller fish species but most aesthetically pleasing. |
|
Rain Collection Tanks |
Collect rainwater or farm plants & fish. |
|
Rain Barrel |
Smaller tanks for balcony or urban gardening. |
|
Bathtub |
Versatile for indoor and outdoor aquaponics setups. |
Repurposing fish tanks is popular due to environmental concerns. People are creative and think of everyday items as components of their own self-sustaining ecosystems. Size matters for aquaponics fish tanks - you don't want them to feel cramped!
Minimum Gallon of an Aquaponics Fish Tank
The size of an aquaponics tank is key for a healthy, sustainable system. Here's what to consider when choosing the minimum gallon capacity:
- For filtration and waste management bigger is better and but harder.
- For temperature/pH stability bigger is better and easier but more costly to heat.
- Start small, adapt as you go.
- For learning: start with a 1-gallon tank.
- For self-sufficiency: aim for 100-200 gallons.
- For a family of 4: 250-500 gallons.
Plus, certain fish species need their own space. Researching them helps to determine the right gallon capacity.
An example: An aquaponics enthusiast once started small with a 10-gallon tank. Gradually, he built up to over 500 gallons. His experience taught him that starting small and adapting is best. Many mistakes he made with a small system prevented them from being made with a big system. Now, he enjoys a bountiful harvest from his self-sustaining system. So, pick your tank size like you would a joke: not too small, not too big and DIY.
Maintenance and Cleaning related to Fish Tank Size
Maintaining and cleaning a fish tank in an aquaponics setup can depend on its size. Here are 3 points to ponder:
- A larger tank needs less maintenance than a smaller one. The bigger volume of water keeps the temperature, pH levels, and nutrient distribution more stable. So, less cleaning and maintenance is needed to support the fish and plants.
- Use an automated system to decrease the need for manual tasks. It helps regulate water flow, ensures water quality, and even feeds the fish. This gives a virtually maintenance-free experience, with healthy fish and plants.
- Bigger tanks are cleaner. The waste produced by the fish gets diluted better in more water. So, there is less time spent on cleaning filters or removing debris.
Size of the tank and using automated systems can drastically reduce maintenance needs. It also ensures optimum conditions for aquatic success.
Have you ever repurposed an item for your aquaponics fish tank? Share your creative ideas in the comments below!
Still not sure? Then use IBC Container, made for transport, it's sturdy and has standardized accessories.